The Economics of Good Soil Health [Why Soil Health Testing Pays Off]
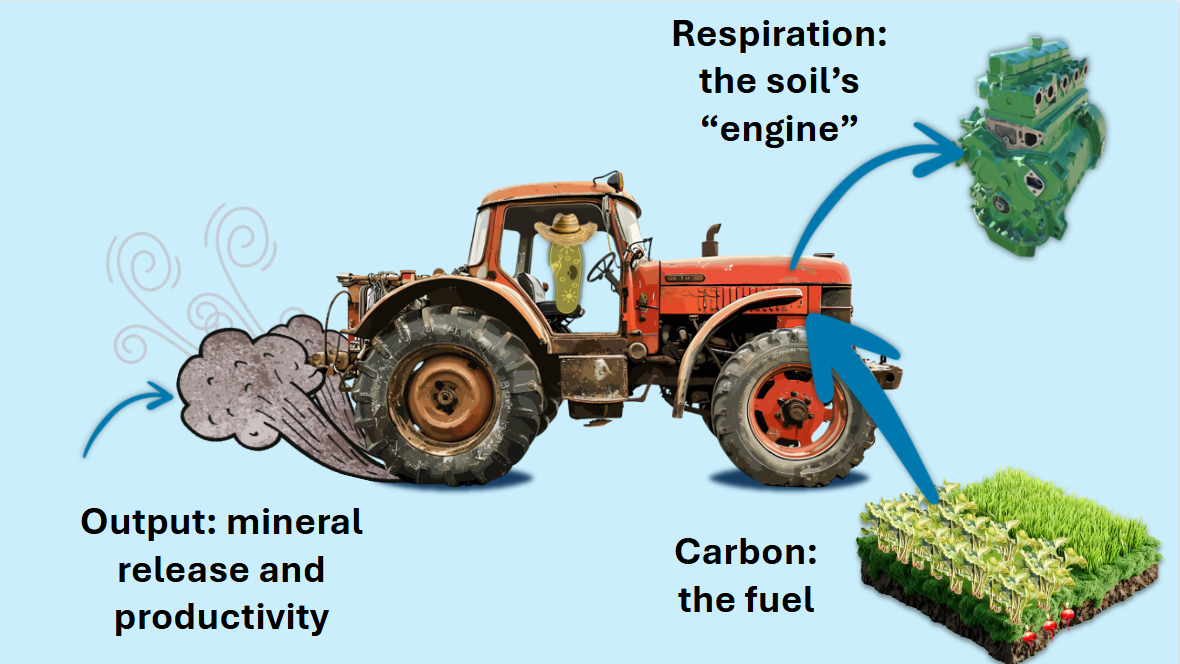
The economics of good soil health is one of the most critical factors in sustainable and profitable agriculture. Yet, many operations overlook the hidden costs of not testing their soil. At Ward Laboratories, Inc., we help farmers and agribusinesses make [...]



